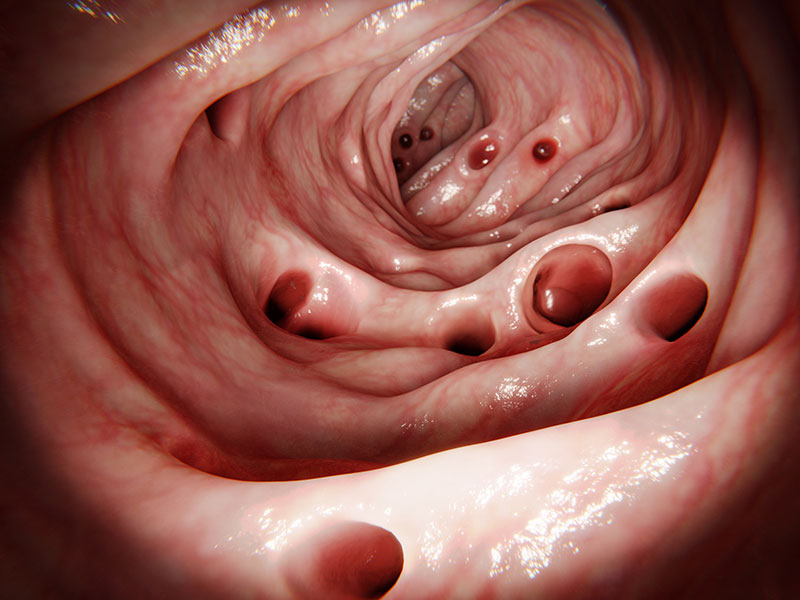
While many people carry diverticula in their sigmoid colon, only 10-15% of these individuals develop symptoms over time. The most common problem that occurs, is an inflammation of one or several diverticula and the adjacent piece of the colon. This inflammation can extend into the surrounding of the colon and the extent and degree of this inflammation usually determines the necessary treatment.
Recurrent and even minor inflammation can cause a scaring of the bowel leading to a narrowing and stenosis of the bowel lumen, that can hamper to passage of stool through the bowel and lead to obstruction and constipation. If medical regulation of bowel movements fails, surgical intervention might be indicated.
As diverticula protrude through small gaps in the muscular layer of the colon, through which also blood vessels find their way through the bowel wall, diverticula can also cause severe bleedings, with significant perianal loss of blood. If such a bleeding cannot be stopped during endoscopy, surgery might be required in rare case.